Cytochrome P450
Cyp450 catalyzes the oxygenation of lipophilic drugs/substances making these more hydrophilic.
Cyp450 subfamily 1-3 are predominantly involved in the metabolism of xenobiotics/commercial drugs (reviewed in: Ma and Lu, 2011).
Cyp450 subfamily 4 and higher are predominantly involved in the metabolism of endogenous substances such as fatty acids, steroids and endocannabinoids (Fer et al., 2008).
The most important human cyp450’s are:
-
Cyp2D6:
-
Cyp2C9:
-
Cyp2C19:
-
Cyp3A4:
-
Cyp3A5:
For a full overview of human CYP450 alleles/polymorphisms, please see: http://www.cypalleles.ki.se/
For a full overview of drug interactions with the major CYP450 alleles, please see: http://medicine.iupui.edu/CLINPHARM/ddis/main-table
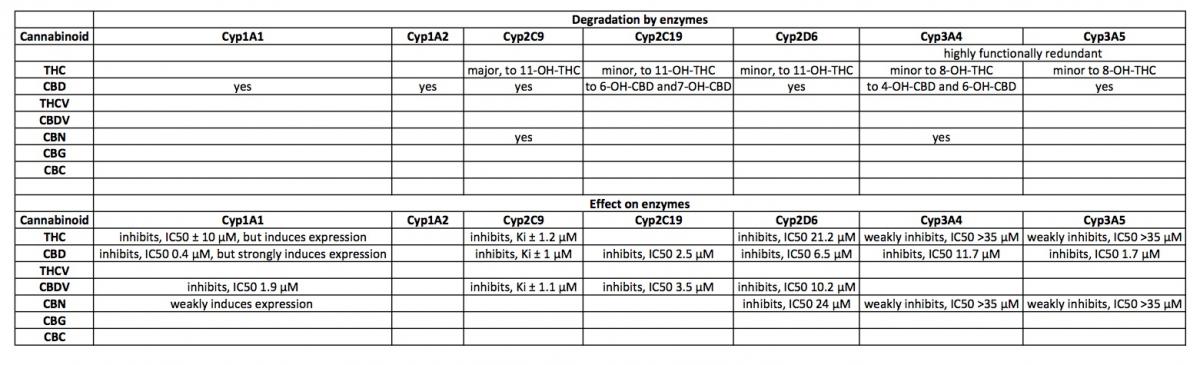
Metabolism of plant cannabinoids:
THC is converted to 11-OH-THC by Cyp2C9, Cyp2C19 and Cyp3A4.
11-OH-THC is further converted into over 30 secondary metabolites, mostly by UGT enzymes (Gaston and Friedman, 2017).
CBD is converted to 7-OH-CBD by Cyp2C19 and Cyp3A4 and potentially by Cyp1A1, Cyp1A2, Cyp2C9 and Cyp2D6 (Gaston and Friedman, 2017).
CBN is primarily oxidized by Cyp2C9 and Cyp3A4 (Yamaori et al., 2011).
Inhibition of Cyps by cannabinoids:
Cyp2D6 is inhibited by THC (IC50 21.1 μM), CBD (6.5 μM) and CBN (24 μM)(Yamaori et al., 2011).
NB, although CBD is a relatively strong inhibitor of Cyp2D6, this effect probably occurs at relatively high doses (200mg or higher, estimated from: (Yamaori et al., 2011)).